Is your website lagging behind on Google? Or is it performing well and you want to find out how you can do even better? We’re taking a deep dive into what makes a well SEO optimised website, and how you can test your site yourself to find out your website’s true SEO strength.
Measuring Success
Before we get into the SEO side of things, you should have a clear idea of your goals for your business and your website. Whether it’s to gather interest in the products & services you sell and get your users to convert, or to get your audience to get in touch with you by the way of an online contact form.
Google Analytics
One of the main ways to track your website performance is by using Google Analytics. This should be one of the first things you set up when you launch a new website. As it records all the traffic to your site, from various sources. Google Analytics is one of the most important tools for SEO, as you can analyse how many people are visiting your site from search engines, and assess which pages on your sites are being engaged with the most, among other things.
Key Metrics
There are a variety of metrics that will come in handy when using Google Analytics, it’s worth knowing what each of them means and how they help you determine your overall website performance.
Users
The number of unique users who visit a page on your site.
Sessions
A group of interactions one user takes within a given timeframe on the website.
Pageviews
The number of times a webpage has been loaded in a browser. (This is often far higher than users and sessions).
Pages/Session
The number of pages viewed in a session.
Average Session Duration
The average amount of time of each session. (Users can have more than one session).
Bounce Rate
The percentage of single-page sessions, which end without the user interacting with the website. If your bounce rate is consistently high, then it’s worth investigating as users aren’t engaging with your content.
Source/Medium
This metric is one of the main ones you should be looking at when you analyse where your website traffic is coming from. The source is the origin of the traffic, so for example, Google.co.uk, or Facebook.com. The Medium is what category the source falls into, which is broken down into; Organic Search, Direct, Paid Search, Referral, Social.
Goals Completed
Goals are user-defined metrics which report on a specific event. For example, if a user filled in and sent a contact form, that could be counted as a Goal. (Goals need to be set up manually).
Goal Conversion Rate
The percentage of users who successfully complete a goal on your site.
Goals & Their Importance To Measuring Success
Goals are a great way of measuring how engaged your users are with the website. Goals can be defined in a variety of ways. As we’ve mentioned above, a contact form completion could be set a goal. However, there are plenty of other things that you could track, for example, if a user clicks on an email address, or if they scroll to a certain position on the page.
Goals such as contact form completions, need to be added to the website as an event. This can be down by editing the Google Analytics tracking code with the Goal information. However, we would recommend using a tool such as Google Tag Manager which makes it easier to add code snippets to your website.
How To Measure Traffic Levels
As we mentioned previously, Google Analytics allows you to see which medium your website traffic falls into, from Organic Search to Social traffic. This allows you to see which medium is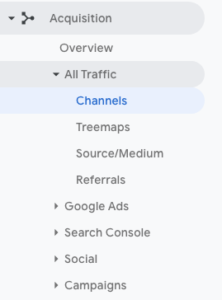 bringing the most traffic to your site, and which ones aren’t.
bringing the most traffic to your site, and which ones aren’t.
In Google Analytics, if you click on the Acquisition panel, it will expand and bring up some different options. Underneath All Traffic, there is an option called Channels. This will bring up a graph which will show you where your traffic is coming from. This is extremely useful when analysing how your website performs online.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is one of the best tools you have to manage your website. GSC allows website owners to list their website on Google and measure the performance of the website. It will also let owners know of any major issues that could be affecting SEO performance. We would recommend that you list your website on Google Search Console as soon as possible if you haven’t already.
Mobile-First Indexing
Mobile-First Indexing is a term coined by Google to explain that Google now crawls websites using their mobile crawler, rather than their desktop one. What this means for you and your website is that Google will now look at the mobile version of your site first, and make ranking & indexing decisions based on this. So if your website isn’t mobile-friendly, you may start seeing ranking positions decrease or you might struggle to climb the rankings.
You can find out if your website has mobile formatting issues by using Google Search Console.
Setting Search Console Up
There are multiple ways to set up Google Search Console, and they’re all relatively easy to do.
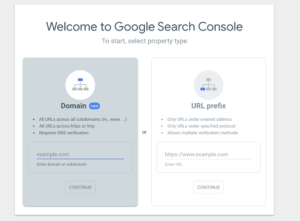 When you first sign in to Google Search Console, you’ll be greeted by this screen. There are two property types. You can verify your whole domain if you are able to completed DNS verification. For this example, however, we’re going to use the URL prefix option.
When you first sign in to Google Search Console, you’ll be greeted by this screen. There are two property types. You can verify your whole domain if you are able to completed DNS verification. For this example, however, we’re going to use the URL prefix option.
Once you’ve entered your website URL, you’ll be greeted with 5 options on how to verify your website. If you’re using the same Google account as the one under your Google Analytics account, you’ll be able to verify it without any extra work. The same goes for Google Tag Manager.
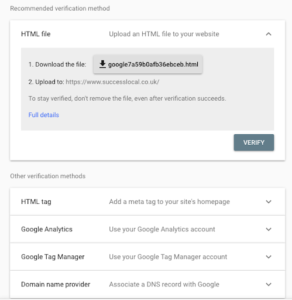 The 3 other options are; uploading a HTML file to your website, which you’ll need FTP or cPanel access for; adding a HTML tag to your site, this can be done in a variety of ways, but we’d recommend FTP; or you can associate your website’s DNS record with Google.
The 3 other options are; uploading a HTML file to your website, which you’ll need FTP or cPanel access for; adding a HTML tag to your site, this can be done in a variety of ways, but we’d recommend FTP; or you can associate your website’s DNS record with Google.
If you have an SSL certificate, you’ll need to do the same again with the 3 other variations of your website. So for example, HTTPS/HTTP & www./non www.
If everything was done correctly, your website should now be fully listed on Google Search Console.
Search Console Errors & How To Diagnose Them
Search Console will alert you of any errors and issues found when crawling your site. This can make it far easier to know what needs improving on your site. We’ve compiled some of the most common errors that appear.
Pages Are Blocked By Robots.txt
This happens when your robots.txt is blocking the page that Google is trying to crawl. The robots.txt is a file on your website which tells internet crawlers the rules when crawling your site.
For example, you may want to block a certain area of your site from bots & crawlers because you don’t want this to be found on Google.
This could for a legitimate reason but we would recommend testing your robots.txt here to make sure that your robots.txt is configured correctly.
Page Is Marked No-Index
No-indexing is a term we use in the industry to tell Google and other search engines not to index (or show) that page or website in the SERPs (Search Engine Results Page).
No-indexing is often done on purpose, to prevent Google from showing a page. For example, if you’re rewriting on an old blog post but you don’t want people to find it until you’re finished with it. If you want the page to be indexed, you’ll need to remove the no-index tag from the page.
Submitted URL Not Found (404)
This happens when a page that was submitted to Google and possibly indexed at one point, is no longer available because the link goes to a dead page, or commonly known as a 404 error.
This happens for a variety of reasons. You may have deleted a page on your site and forgot to redirect it to somewhere else on the site. You might hide a post or page so you can edit it, but forget to add a temporary redirect to it. You can fix this error by reinstating the page to its original state or redirecting the page to a different part of the site.
Mobile Usability Errors
As we mentioned earlier, Google is putting a bigger emphasis on mobile websites. If your website has mobile usability issues, Google will give you an idea of why. There are a few different errors that you may receive.
Text Too Small to Read
Your text is too small to read on a mobile device, this may require changing the font size when using a mobile device to make the text more legible.
Clickable Elements Too Close Together
Buttons and other clickable elements are too close together, a user may accidentally click on the wrong element. This may require changing how your mobile layout works, to help the user have a pleasant experience while browsing the website.
Manual Actions and Their Effects
Manual Actions are Google imposed sanctions on your website. These sanctions are brought upon your site when a human reviewer believes your site is not following Google’s webmaster quality guidelines. There are a few different reasons why your site would have manual actions, such as; unnatural links to your site, hidden text and/or keyword stuffing, and plenty of other reasons.
Manual actions can lead to specific pages of your site being deindexed or potentially even your whole site. This will likely lead to a drop in traffic and a loss in conversions/sales. If you have a manual action on your site, Google will advise you on what to do next. This will require you to fix or remove the issues from your site and then request a reconsideration request.
Bing Webmaster Tools
Similar to Google’s Search Console, Bing Webmaster Tools is how you submit your site to Bing. The features included are very similar to what Google has on offer. This is made even easier because Bing allows you to import your Google Search Console listing straight into Webmaster Tools, so you don’t have to manually verify the website.
Google Business Profile & Bing Places
Google Business Profile (formally known as Google My Business) is a must-have tool for local businesses. GBP allows you to list your business on Google & Google Maps free of charge. It’s relatively easy to set up and it’s a necessity for Local SEO. Bing Places is the same tool but on Bing’s platform rather than Google. Much like with Google Search Console, you can import your Google Business Profile listing into Bing Places with ease. These means you don’t have to go through the long-winded verification process twice.
Your Google Business Profile listing has the chance of appearing on Google’s Map Pack, which displays relevant businesses dependent on the user’s query and location.
Setting Up a Google Business Profile
If you haven’t already set up a Google Business Profile, we would recommend you do so immediately, as it takes up to 14 days to verify your listing. Once your listing is verified, you can then import your Google Business listing into Bing Places.
Mobile-Friendly Websites
We covered it briefly in the Google Search Console section, but mobile-friendly websites are more likely to perform better than non-mobile-friendly websites, due to Google’s switch to Mobile-First Indexing.
If you’re not sure why having a mobile friendly website is a big deal, well around 52% of global internet traffic comes from mobile devices. Not having a mobile website can impact your organic search rankings, as well as decrease the amount of visitors you have on mobile devices as users are less likely to convert on a mobile device if your site isn’t responsive/mobile-friendly.
How To Test Your Website
One of the easiest ways to test if your website is mobile friendly, is to use Google’s Mobile Friendly Tester. If your website isn’t mobile friendly or has multiple issues, we would encourage thinking about a website redesign to make sure your website incorporates a responsive design.
Keywords
Picking the keywords to optimise for is a tricky task for many people. As it means you’ll have to prioritise certain aspects of your business over others. Our trick is to pick the services you provide, and the locations you cover. So for example if you’re a removal firm in Leicester. One of the main keywords/phrases you’ll want to optimise for is ‘Removals Leicester’. We recommend you do this for each of the services you provide as well as the locations you cover.
How To Track Keywords
There are multiple ways to track keywords. There are paid tools such as Moz, SEMrush and others, but we understand you might not want to pay for these services. So there are a couple of options available to you.
Searching Google in Incognito
We can’t stress enough that you’ll need to open an incognito tab in your browser for this to work correctly, otherwise you’ll have your own personalised results factored into the search. Searching in Incognito will allow you to get the most accurate results for your location. However if you’re searching for terms outside of the area you’re located, the results may be slightly skewed.
Using a Free Third Party Tool
There are plenty of third party tools out there which enable you to see your live rankings. However the majority of them are paid tools, and they aren’t cheap either. There is a free Google Chrome extension called FATRANK, which enables you to see your current rankings on the page you’re currently on.
On-Site SEO
On-site SEO is a term for the process of optimising the elements of a website, rather than optimising for links on other websites. To measure your on-site SEO performance, you’ll need a crawler of some sort. There are plenty of free crawlers (that have limits) out there, however we recommend using Screaming Frog, as it’s an in-depth crawler with a lot of functionality, and the free version allows you to crawl up to 500 pages. We’re going to go through the key areas of on-site SEO.
Meta Titles & Descriptions
Meta Titles & Descriptions are some of the most important elements of a successful SEO campaign. They can help influence users to click onto your site, as well as help rank your site higher on Google.
Meta Titles can influence your search engine rankings, as they help tell Google & users what your page is about. Meta descriptions don’t influence rankings, but they can contribute to an increased clickthrough rate.
Character Limits
There are character limits imposed on both the Meta title & description. These should be followed to make sure your listing is as optimised as possible. Meta titles have a max limit of 60 characters, and descriptions have a max limit of 160 characters.
How To Check and Test Your Meta Titles and Descriptions
The best and most efficient way to test your meta is to run your website through a site crawler such as Screaming Frog.
Page Structure and Content
Content should be the crux of your SEO strategy, as without quality content, your website is doomed to fail before it even starts. Having high-quality, unique, relevant content sets you apart from your competitors and Google will see that. High-quality content can also encourage users to link to your site, which then increases your backlink profile and Domain Authority.
Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing is the practice of stuffing relevant keywords onto a page in order to get it to rank. This will consist of keywords being shoehorned into the content, even though there’s no context or reason for them to be there. Google has become pretty good at detecting keyword stuffing so it’s really worth the risk.
Keyword stuffing also detracts from the user’s experience as the content won’t make much sense when certain keywords have been stuffed into the content. You want your content to be easy to read and understand.
Headings and Their Importance
Headings are quite important to page structure and helping search engine bots decipher what the content is about. You should only have 1 H1 on a page, as these can help with your SEO.
H2’s & H3’s, etc are less important but it is worthwhile structuring your content with these subheading types.
How to Check
Checking your content is relevant and unique should be a manual task, where you read through the content itself. Checking the page structure of all your pages is best done with crawlers such as Screaming Frog, or a free site auditor tool.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is the process of optimising the elements of the website which help Search Engines crawl and index the site. This also includes making sure the site runs smoothly and fixing any page errors (broken pages) when they arise.
Redirects/Page Errors
When you delete a page or change the URL of a certain page or post, if not redirected, the page in question will 404. This can lead to a severe impact on SEO performance if left unfixed.
In order to fix a broken page, you have a couple of options. You could reinstate the old page that you deleted (or changed), if the removal/change was accidental. However in most cases, you’ll need to redirect the broken page to a new page. This is to ensure that the user’s journey on your site doesn’t get interrupted, as they are more likely to abandon their journey if they land on a 404 page.
3XX Redirects
Response codes with a 3 indicate that a redirect is happening. While there are multiple 3XX codes, there are only a few you’ll need to know.
301 Redirect
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect, this tells search engine crawlers that the page which is being redirected, won’t be available again. This is the type of redirect you should use in most cases.
302 Redirect
A 301 redirect is a temporary redirect, this tells crawlers that the page which is being redirected may be available again at some point. This should be used in cases such as if you are testing a new page, but you want to leave the original page intact and not impact its rankings.
4XX Errors
Response codes with a 4 indicate there is a client error and the page isn’t available. In the majority of cases, these should be fixed ASAP. 4XX errors can negatively impact your SEO performance so we recommend you clear these errors as soon as you can
404 Error
A 404 error appears when the page you’re trying to get to no longer exists. This could be because of a change of page structure, a page has been deleted or the URL has changed. These types of errors can severely impact your SEO performance so it’s important you fix these errors as soon as possible. A good habit to get into is to redirect any page that you delete or change the URL of, this way your back is always covered.
5XX Errors
Response codes with a 5 indicate there is an issue with the server, this could be due to an overload of traffic, or a misconfiguration of the server. These kinds of errors should be dealt with as soon as possible, but it may be necessary to get in touch with your hosting provider to figure out the problem.
How To Test and Check
You can use a crawler such as Screaming Frog to identify any broken links or server issues. Google Search Console will also report any page errors in the platform, so it’s worth checking there as well.
Robots.txt and XML Sitemaps
A correctly defined robots.txt can be the difference from appearing on Google, and not appearing at all. A robots.txt is a file on your website which tells web crawlers which pages can be accessed and which areas of the site should be left alone.
An XML sitemap acts as a roadmap of your site, that tells search engine crawlers where all of your important pages are. They are good for SEO as they allow search engines to swiftly find all of your important pages.
Example of an optimised Robots.txt
Each site’s robots.txt will be different as every website is built differently. However there are common conventions that should be followed. Please see Success Local’s robots.txt below as an example.
https://www.successlocal.co.uk/robots.txt
Example of an optimised xml sitemap
There are many ways you can create a sitemap, there are online tools which allow you to create an XML sitemap. There are also plugins for WordPress which allow you to customise and show an XML sitemap on your site. Please see Success Local’s XML sitemap as an example. Our sitemap was created using the Yoast SEO WordPress plugin.
https://www.successlocal.co.uk/sitemap_index.xml
How to Check
Because each site is different, we can’t give you a definitive guide on how to check your robots.txt and sitemap. However there are a couple of ways to check. To check your robots.txt, you can type your URL into the search bar, and add /robots.txt to the end of the URL. This should take you to your Robots if you have one.
Checking for a sitemap is very similar, just add /sitemap.xml to your URL and it should take you to one if there is.
URL Structure
Your URL structure can have a big impact on the way Google and other search engines look at your site. If they find it hard to crawl, you could see negative performance on SERPs. To achieve the best SEO results, you’ll want your site to be structured in a way that is easy to make sense of and correctly shows the hierarchy of your site.
Nesting URLs
Nesting is the term for structuring URLs in a specific way, to make it clear which subdirectory you are in. So for example one of your URLs might be /digital-marketing. We could nest search engine optimisation under that URL, like so – /digital-marketing/search-engine-optimisation, rather than https://your-website-name.co.uk/search-engine-optimisation.
URL Length
While this isn’t a major factor in helping your site rank better, longer URLs tend to hinder your SEO performance. So having a url such as https://your-website-name.co.uk/this-is-an-example-of-a-extremely-long-url-and-it-doesnt-look-very-good/ is a bit of a nightmare for users to type into the URL address bar and it’s not very optimised in terms of SEO.
How to Check
You can check your URLs by going onto your site and go through all the pages, however this can be quite time consuming so we would recommend using Screaming Frog for this task.
Off-Site SEO
Off-site SEO is the process of optimising for SEO outside of your website, so by increasing your backlink profile and optimising local citations. Off-site SEO is often relegated to the backburner for many businesses. However it is extremely important and beneficial for websites as it can help increase your SEO performance.
Domain Authority
Domain Authority is a proprietary metric created by Moz, which is used by thousands of websites across the world. While DA isn’t a metric used by Google, it is a good indicator of the trust and authority of your website.
Competitor Analysis
DA is an extremely valuable metric for comparing your website against your competitors. As it allows you to see the trust and authority that your competitors have. It also ties in nicely with link building, which we’ll be covering next.
Backlink Profile
A backlink profile is basically the number of links you have pointing to your site from external sources. A good backlink profile will have a large amount of links from a variety of different sources.
Low-Quality Links
Spammy and low-quality links can dilute the power of your backlink profile, if you have too many bad links, Google could potentially derank your site, as they see it as not being trustworthy enough and bad for users. However, Google has become proficient at detecting and ignoring spam links, so in most cases, your site will be okay.
Disavowing
If your backlink profile is full of bad/spammy links, you can create a Disavow file and upload that to Google Search Console. This file will tell Google you don’t want your site to be affiliated with these links. Google also recommends that you get in touch with the link owners to see if you can remove them.
Disavowing should only be a last resort measure, as if it’s not done right, it can seriously harm your organic presence.
Local Citations
Local Citations are critical for ranking well locally. They are mentions of your business and website across local directories and other local platforms. Citations can help users discover your local business and can impact local search engine rankings. We would recommend you check for any mention of your business on a variety of platforms, and make sure your information is correct. It’s easy to make a mistake and send a potential business to the wrong address or phone number.
How To Check For Backlinks
There are a few different ways to check your backlink profile, however some of the options aren’t free.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console has a dedicated area to assessing links to your site. You can export a sample of those links to assess who links to you. This option is limited though as Google doesn’t give too much information.
Third Party Tools
There are multiple third party tools which enable you to see the links to your site in more detail than what Search Console offers. Unfortunately these tools aren’t cheap. If you’re looking to invest in one of these tools, we would recommend investigating Majestic, Moz and Ahrefs, as these are some of the most powerful tools out there for backlink profile research.
Making a Priority List
So now that we’ve gone through each section, it’s now time to create a priority list of the tasks that need doing. These should be sorted out as high, medium, low priority tasks. All of these tasks are integral to good SEO performance.
High priority tasks would include fixing broken links and setting up a Google My Business profile.
Medium would include optimising your Meta titles and checking your content.
Low priority would include optimising your meta descriptions and checking your URL structure, but these tasks are still extremely important. This list should help you identify which areas of your website you should work on first.
The Importance of a Comprehensive SEO Strategy
You can’t just climb the rankings by optimising one aspect of your site. A good SEO strategy incorporates all sides of SEO. It’s not worth neglecting one aspect of SEO to optimise for another. By determining your website’s SEO strength, you’ll be able to clearly identify which areas of your site need to be worked on.
If you’re struggling to optimise your site for SEO best practises, having a hard time assessing your website’s SEO strength or require some digital marketing expertise then the friendly team at Success Local are happy to help. Feel free to give us a call on 01455 36 7100 or email us via our contact form.
Posted in Advice
